

HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language, a standardized system for tagging text files to achieve font, colour, graphic, and hyperlink effects on World Wide Web pages.

CSS Stands for Cascading Style Sheets. CSS is the language for describing the presentation of Web pages, including colors, layout, and fonts. It allows one to adapt the presentation to different types of devices, such as large screens, small screens, or printers. CSS is independent of HTML and can be used with any XML-based markup language.

a user is a person who browses the internet

A combined device for modulation and demodulation, for example, between the digital data of a computer and the analogue signal of a telephone line.
A network is a system that everything one the system would be concted to one another
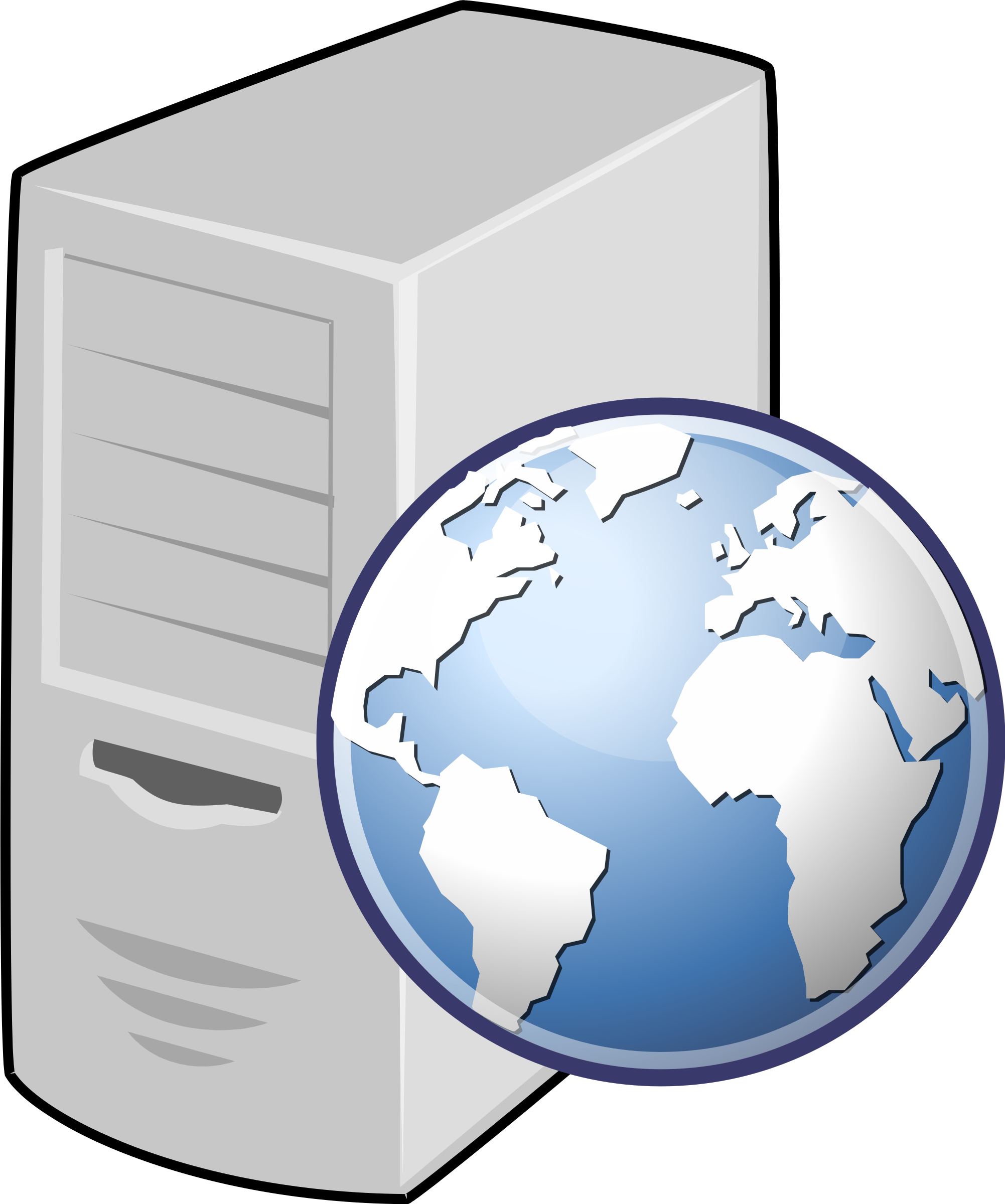

A Web server is a program that uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to serve the files that form Web pages to users, in response to their requests, which are forwarded by their computers' HTTP clients. Dedicated computers and appliances may be referred to as Web servers as well.
A Device can be a Computer,Phone,Laptop,Ipad and can connect to the internet

an information system on the Internet which allows documents to be connected to other documents by hypertext links, enabling the user to search for information by moving from one document to another.

A Web browser, or simply "browser," is an application used to access and view websites. Common web browsers include Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari. The primary function of a web browser is to render HTML, the code used to design or "mark up" webpages
A hypertext document connected to the World Wide Web.
an arrangement of intersecting horizontal and vertical lines.
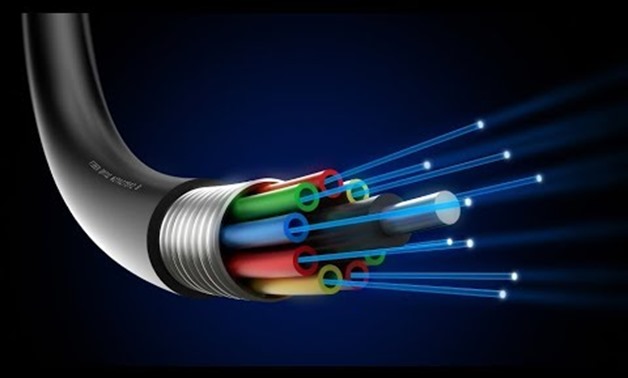
Imagine what they'd make of modern fiber-optic cables—"pipes" that can carry telephone calls and emails right around the world in a seventh of a second! Photo: Light pipe: fiber optics means sending light beams down thin strands of plastic or glass by making them bounce repeatedly off the walls
URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) and IP addresses are just identifiers used for this purpose. The main difference between URL and IP address is what they point to. An IP address basically points to a computer, whether it is the physical hardware or a virtual one as in the case of shared hosting
The most common programming languages on the Web include HyperText Markup Language, JavaScript, Cascading Style Sheets and PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor. Some are used in conjunction with each other while some can be used almost entirely separate from the other languages to create an interactive or static website
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably.
A DNS server is a computer server that contains a database of public IP addresses and their associated hostnames, and in most cases, serves to resolve, or translate, those common names to IP addresses as requested. DNS servers run special software and communicate with each other using special protocols.
New domain types are continually being introduced but some should be used with caution and certainly not as a primary website address. most common domain types. The most common international domain names are: .co.uk, .com .net .org .info and .biz.com. These are the safest choices and can be used by almost all websites.

